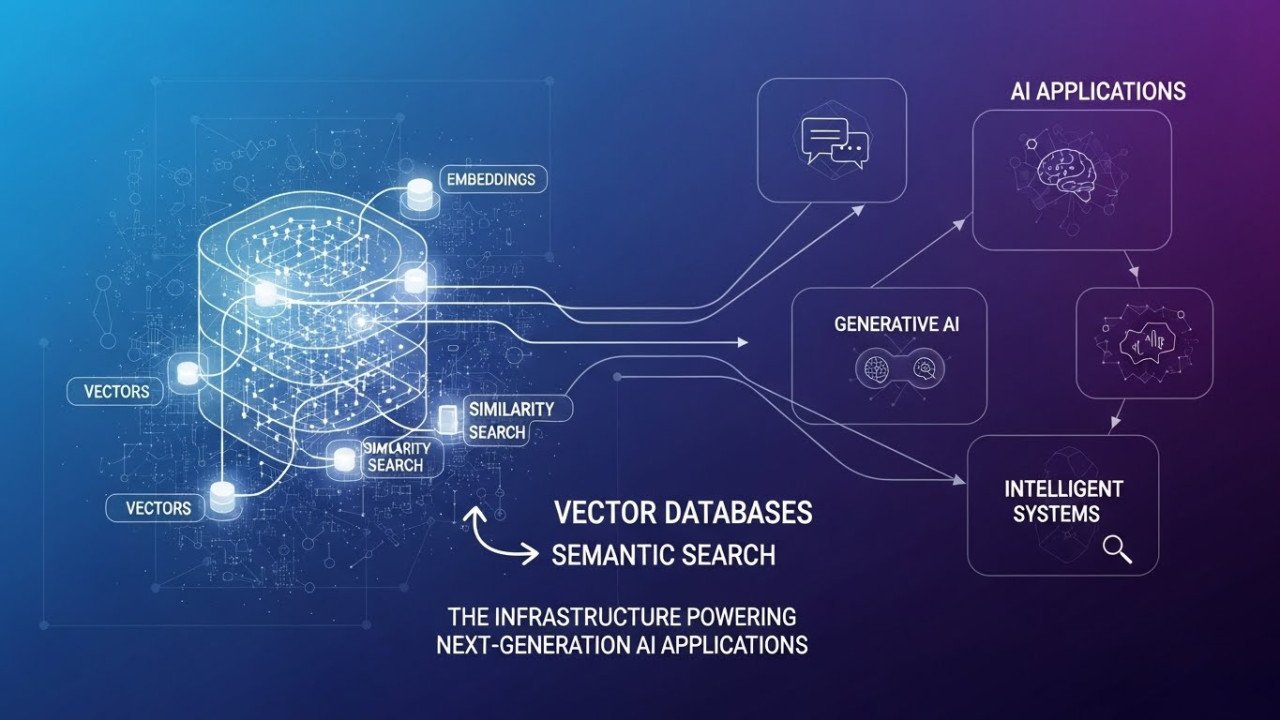
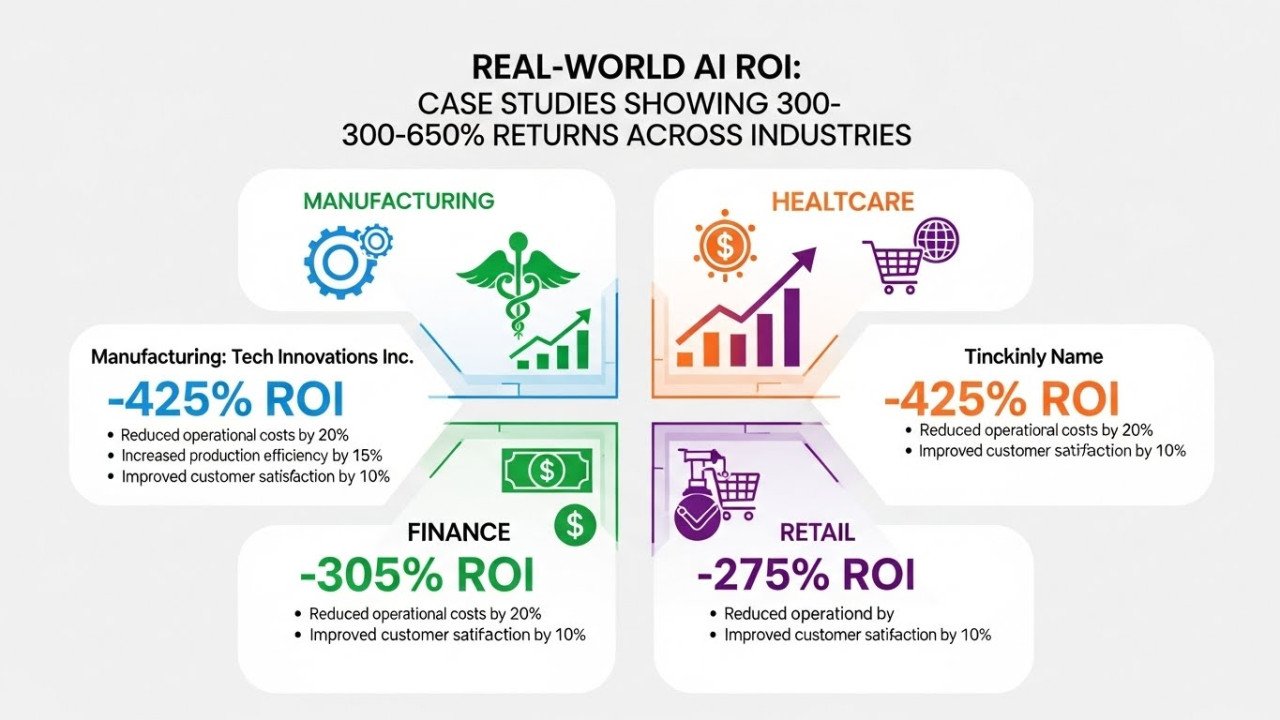
Conversational AI Interfaces: Designing Multimodal Experiences With Voice, Vision, and Gesture
Multimodal conversational AI combining voice, vision, gesture achieves natural interactions with <300ms latency. See design patterns, speech accuracy challenges, and real-world deployment data.